Elevated ductwork generally refers to ventilation ducts installed at high elevations, primarily used in ventilation, air conditioning, and exhaust systems. The following is a detailed introduction to this topic:
Features
High installation location: Elevated ducts are generally installed at the top of buildings, above ceilings, or on steel structures at high elevations to provide ventilation or air conditioning coverage for specific areas.
Efficient use of space: It can deliver air to the required areas without occupying floor space. This is particularly important for places with limited space, such as industrial plants, large warehouses, and gymnasiums, as it can effectively utilize vertical space and improve space utilization.
Long air delivery distance: Due to the high installation position, the air duct can utilize natural air flow and pressure differences to deliver air over long distances, thereby achieving large-area ventilation or air conditioning coverage.
Aesthetically pleasing: Elevated ductwork is typically installed at a height where it is not easily visible to people, thereby minimizing its impact on the appearance of the building and keeping the interior neat and attractive.
High construction difficulty: Installation at high altitudes requires specialized high-altitude work equipment and technical personnel. Safety issues must be addressed during construction, which also increases the difficulty and cost of construction.
Maintenance inconvenience: Due to its elevated position, maintenance personnel need to use professional climbing equipment to perform repairs, maintenance, and other tasks, which increases the difficulty and cost of maintenance and places higher demands on the skills and safety awareness of maintenance personnel.
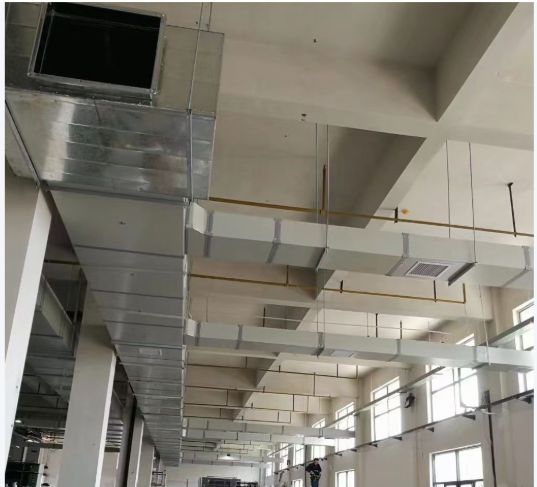

application scenarios
Industrial plants: Used to remove exhaust gases, dust, and heat generated during production, provide fresh air, improve the working environment, protect workers’ health and safety, and also help protect equipment and improve production efficiency.
Large warehouses: such as automated multi-level warehouses, which can control the temperature and humidity of different areas within the warehouse to ensure proper storage conditions for goods and prevent them from becoming damp, moldy, or spoiled.
Commercial buildings: such as shopping malls, supermarkets, shopping centers, etc., used to regulate indoor air temperature, humidity, and air quality, providing customers and employees with a comfortable shopping and working environment.
Sports venues: Able to meet the ventilation and air conditioning needs of large numbers of spectators and athletes in sports venues, ensuring fresh air and comfortable temperatures inside the venue, thereby enhancing the spectator experience and the competitive performance of athletes.
Transportation hubs: such as train stations and airports, can effectively regulate the air environment in areas such as lobbies, waiting rooms, and waiting areas, providing passengers with a comfortable waiting space.
Installation points
Construction plan formulation: Based on the specific conditions of the construction site, including building structure, duct installation location, height, quantity, specifications, and models, formulate a detailed construction plan, clarify construction objectives and construction sequence.
Safety measures: Set up safety warning signs at the construction site, cordon off the construction area, and prevent non-construction personnel from entering. Set up a suitable aerial work platform, ensure that the platform legs are evenly distributed, install guardrails and anti-slip boards, and set up safety nets below the work platform.
Duct inspection and hoisting: Inspect the ducts before construction to ensure that they are free of damage, deformation, and other issues. Set hoisting points based on the length and weight of the ducts, generally at both ends and in the middle, and use special lifting lugs to secure them firmly. During hoisting, a designated person should be in charge to ensure that the ducts are lifted vertically and do not hit nearby obstacles.
Duct connection and sealing: Align the duct ends and ensure that the interface is flat and straight. Use sealing tape, sealant, or flanges to seal the duct system and prevent air leakage. For duct bends and diameter changes, use special elbow components and diameter change pipes, and pay attention to the sealing of the interface.
Installation Quality Inspection: After installation is complete, inspect the installation quality of the ductwork section by section, including whether the ductwork is straight, whether the connections are secure, and whether there are any air leaks. Use professional testing instruments to conduct airtightness tests, airflow and air velocity tests, etc., on the ductwork system to ensure that it meets design requirements.
